- Solve the centerpieces
- Pair similar edge pieces
- Turn only the outer layers, and solve it like a 3x3!
In this video, I teach the Yau Method, which roughly follows this
outline. The Yau method is the most popular 4x4 method and was used to set
the current
world record.
Example Solve
Here is a full solution where I go through some more possibilities of what
can happen.
Step 1. White Center
Make another white center bar somewhere else on the cube, and then join
the 2 bars together.
This step should be completely intuitive, although you may need to
experiment a bit to get used to how pieces move.
Step 2. Yellow Center
Hold the white center on the bottom, and make a yellow center bar
anywhere on the cube.
Make sure to fix the white center if you ever destroy it. Examples:
Move bar away - Fix white center
If the yellow bar is not on the top face, move it onto the top by doing
this:
Make another yellow bar, and then place it under the first bar to move it to the top:
The tutorial video and example solve videos above show some trickier
cases for this step.
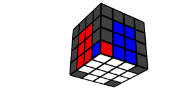
Step 3. Partial White Cross
This step completes 3 out of the 4 cross pieces in the correct
color order.
Hold the white center on the left.
The correct color order going upwards is Blue, Orange, Green, Red (BOGR)
Example of a finished cross and centers:
Find 2 white edge pieces that have the same colors on them.
Put one in the left slice layer, and one in the right slice layer (the
slice layers are the middle 2 layers).
Join them, and add it to the cross.
Repeat this step for a total of 3 (not 4) cross pieces solved, and
follow the color scheme shown above.
Be careful not to destroy other cross pieces or the 2 solved centers.
Step 4. Centers
Make 1 center bar of any color, and turn it to be vertical.
Be careful not to destroy the partial cross (tips explained in the video
tutorial).
If you have completed any other centers already, make sure you also fix
them any time you break them (just like fixing the white center when making the
yellow center).
Make another center bar of the same color.
If this is the first center you've made, you can just join them
together.
If other centers have already been made, but the 2 bars on the same side
to join them:
Solve the rest of the centers.
Some trickier cases for the last 2 centers are shown in the example
solve video above.
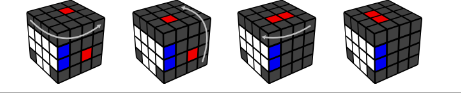
Step 5. Edge Pairing
Hold the cross on the bottom, with the unsolved part at the front.
Look for the last 2 white edge pieces. If one is in the bottom, turn the
front so that it's not.
Put both white pieces in the front/left and front/right without breaking
the partial cross.
Each piece is either on the top or bottom slice layer.
Case 1: If they are indifferent slices:
·
Join the pieces
·
Replace it with an unsolved edge pair
·
Fix the centers
Note: the edge pair coming down must be an unsolved pair.
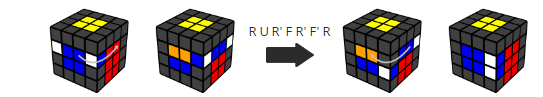
Case 2: If they are in the same slice:
·
Slice piece 1 towards piece 2.
·
Flip piece 1 (with the flipping algorithm: R U R' F R' F' R)
·
Fix the centers
The flipping algorithm R U R' F R' F' R is written in move
notation. Make sure you hold the piece you want to flip at the
front/right.
Insert the cross edge into the bottom layer to complete the cross.
Solve the rest of the edge pairs one at a time using the same method as
for the first edge. If you are ever confused, you can watch the example solve
video above as it shows the full process.
Note: If all the top layer edges are solved already, you can only do
case 2. If you get to case 1 and this happens, flip either of the pieces with the
flipping algorithm to turn it into case 2.
Step 6. Solve Like a 3x3! (mostly)
If you only turn the outer layers, the cube acts like a 3x3 with corner
pieces, edge pieces, and centerpieces.
From here you can solve the cube like a 3x3,
but there are a few problems you might run into:
OLL Parity is when you have a flipped edge that is impossible on a 3x3 and
happens on 50% of solves. You can flip the front/top edge to fix this, by doing
the OLL Parity Algorithm:
Rw U2 x Rw U2 Rw U2 Rw' U2 Lw U2 Rw' U2 Rw U2 Rw' U2 Rw'

PLL Parity is when you have 2 pieces swapped in a way that is impossible on a
3x3, and happens on 50% of solves. This could be 2 corners or 2 edges. To fix
this, do the PLL Parity Algorithm once:
2R2 U2 2R2 Uw2 2R2 Uw2
2R (big cube notation) means to turn the 2nd layer from the right side.
2R2 means to turn that layer twice. This algorithm is also shown at the end of
the tutorial video.
Note: this probably will not solve your case, but doing the algorithm
once makes the cube solvable like a 3x3.
Example (beginner method step 6 impossible
position):
Back to Step 5
Example (PLL impossible position):

Incorrect centers can lead to a weird situation shown below. Even if you follow this tutorial correctly, it's possible that your cube has a different color scheme. You can look at any corner piece to determine how the center colors should be positioned relative to other centers.
To swap the U/F centers: Rw' F2 Rw2 U2 Rw'
To swap the U/D centers: Rw2 U2 D2 Rw2
Next Steps
Congrats on solving a 4x4! The better you get at solving a new puzzle,
the more fun it will get. I highly encourage putting in some practice when you
learn new things, to give it a fair shot at whether or not you'll enjoy it.
4x4 doesn't have a huge amount of advanced techniques, but 3-2-3 edge
pairing is one of the most important ones. Instead of pairing one edge at a
time, this method solves many edges at once.

.jpg)




















0 Comments